Difference Between Mpers And Mfrs

Pwc alert is a digest of topical financial and business information for clients and business associates of pwc malaysia.
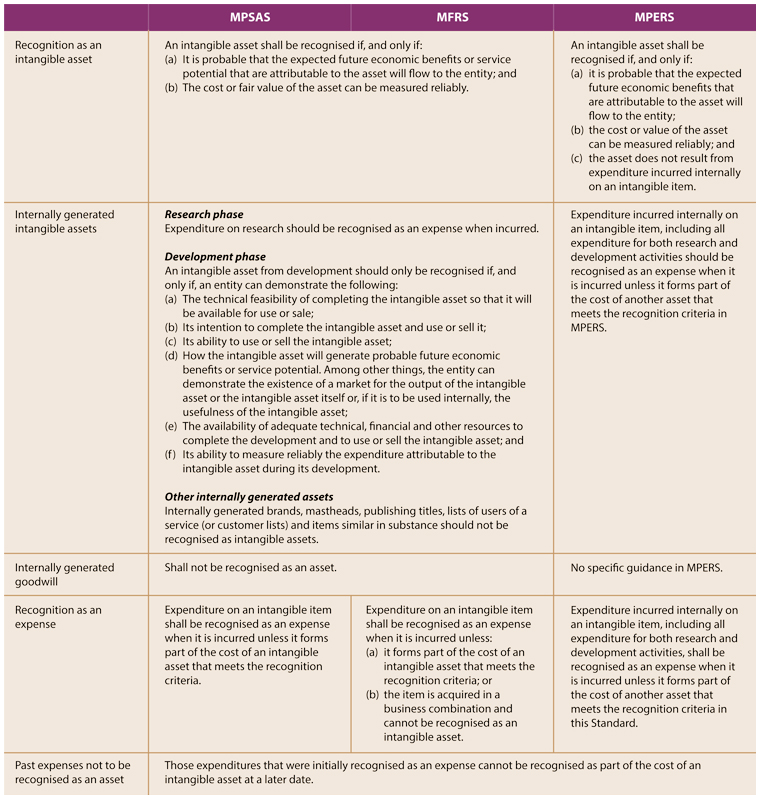
Difference between mpers and mfrs. It highlights some of the key differences with the malaysian financial reporting standards mfrs and the private entities reporting standards pers and analyses the key principles upon first time adoption of the mpers. However under mpsas an entity has to determine whether the asset is a cash generating1 or non cash generating2 asset. Mpers is effective for financial statements beginning on or after 1 january 2016. The weighted mean rank scores of all the three paired comparisons are below the medium level score of 3 0.
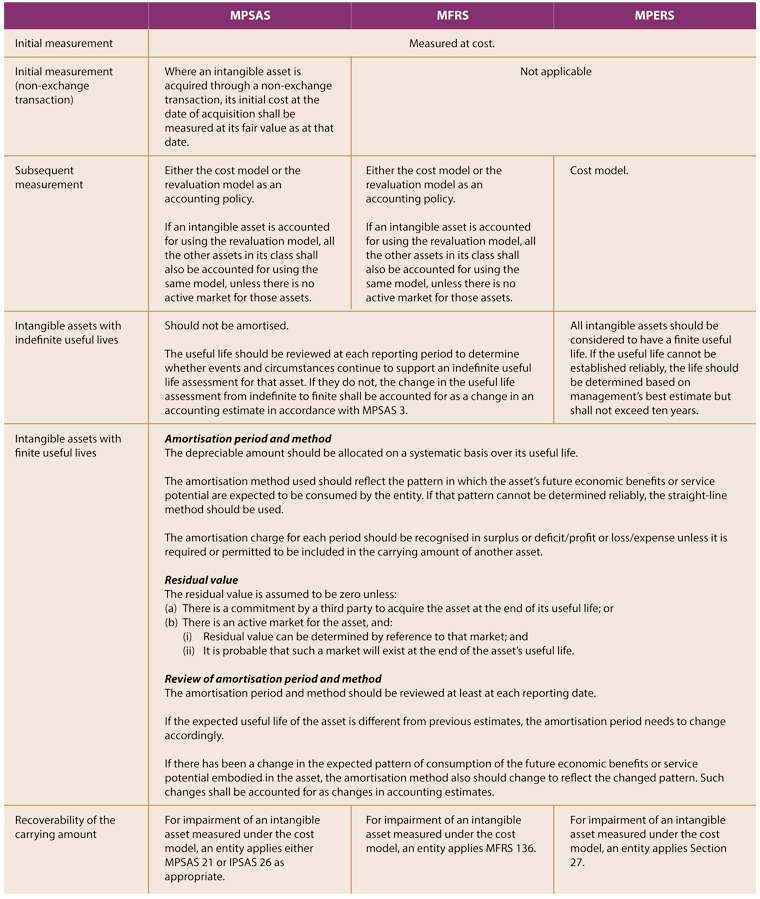
Between pers and mpers the mean rank score is 2 34 and is below the average rank score of 2 50 indicating slightly above the low level of differences between the two reporting frameworks. Mpers requires all borrowing costs to be recognised as an expense in profit or loss while mfrs requires borrowing costs directly attributable to the acquisition construction or production of a qualifying asset to be capitalised as part of the cost of asset. If the asset is a cash generating asset the entity applies the requirements in mpsas 26 impairment of cash generating assets which are similar to mpers and mfrs with no significant differences noted. Although mpers is a replacement for pers a private entity may not necessarily adopt mpers.
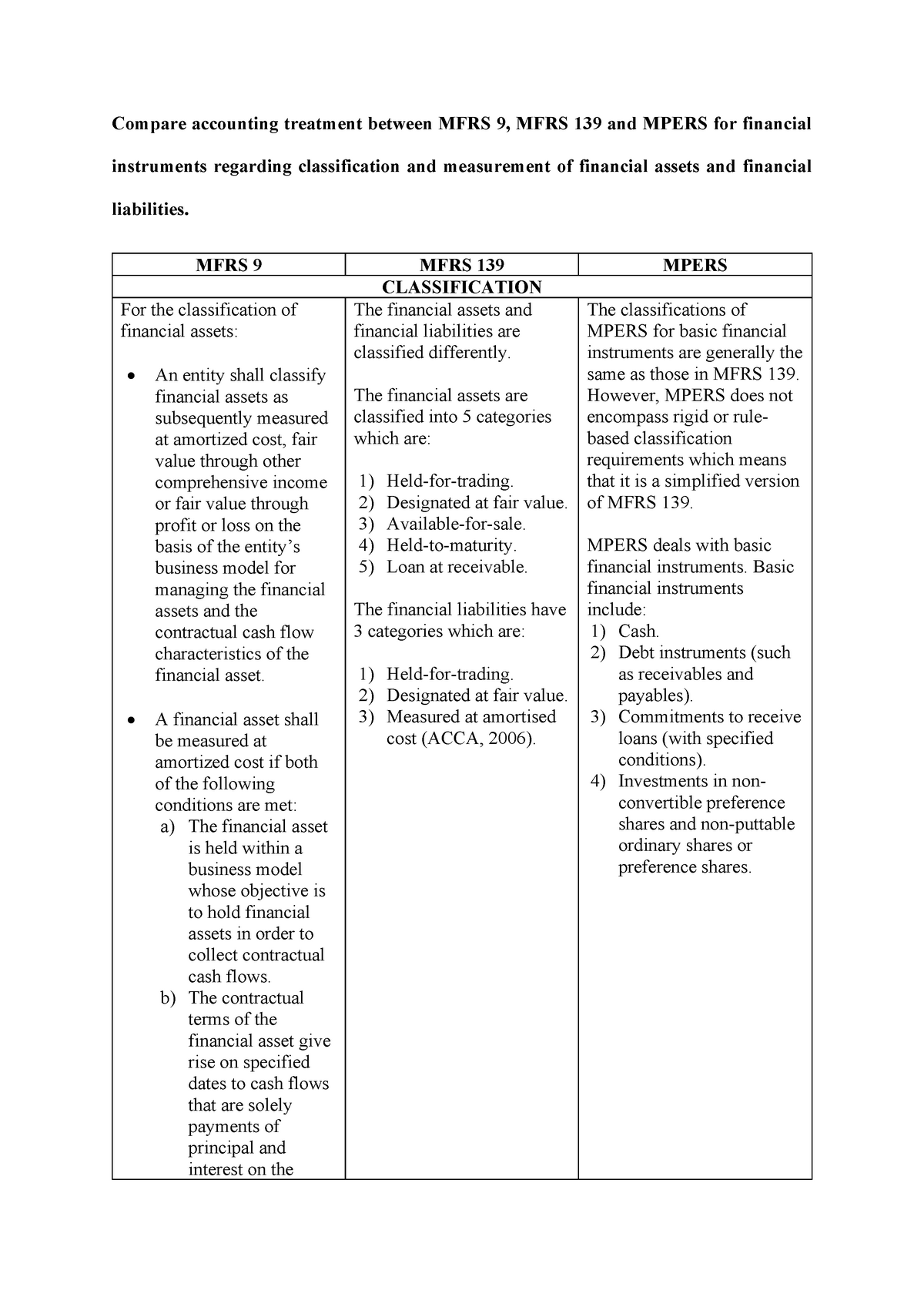
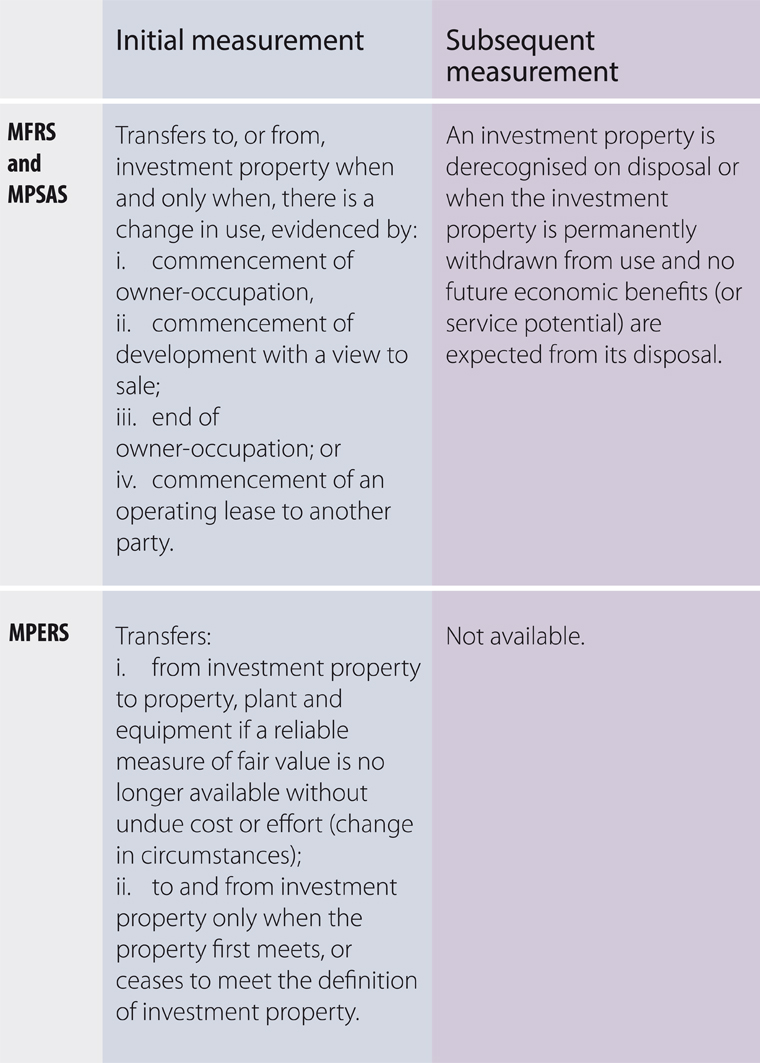
For example in the case of investment property mfrs allows for two models the cost model or fair value model but mpers only allows fair value model hoh said. For impairment both mpers and mfrs have similar requirements. Classification of investments in equity instruments the mfrs 9 s classification of investments in equity instrument is similar to mfrs 139 other than there is no reclassification of gains or losses from oci to profit or loss for example on sale of the equity instrument. The identification of the types of joint arrangemt both pers and mpers use the form while mfrs uses the rights and obligations approach.
Broadly the differences are editorial additional requirements disclosure and transitional provision. Disclosure of fair value information is much more comprehensive in the mfrs including sensitivity test information of significant variables used in the fair value measurement the levels in the hierarchy of fair value measurement and transfers between levels. Mfrs has more detailed disclosure requirements on hedged accounting.